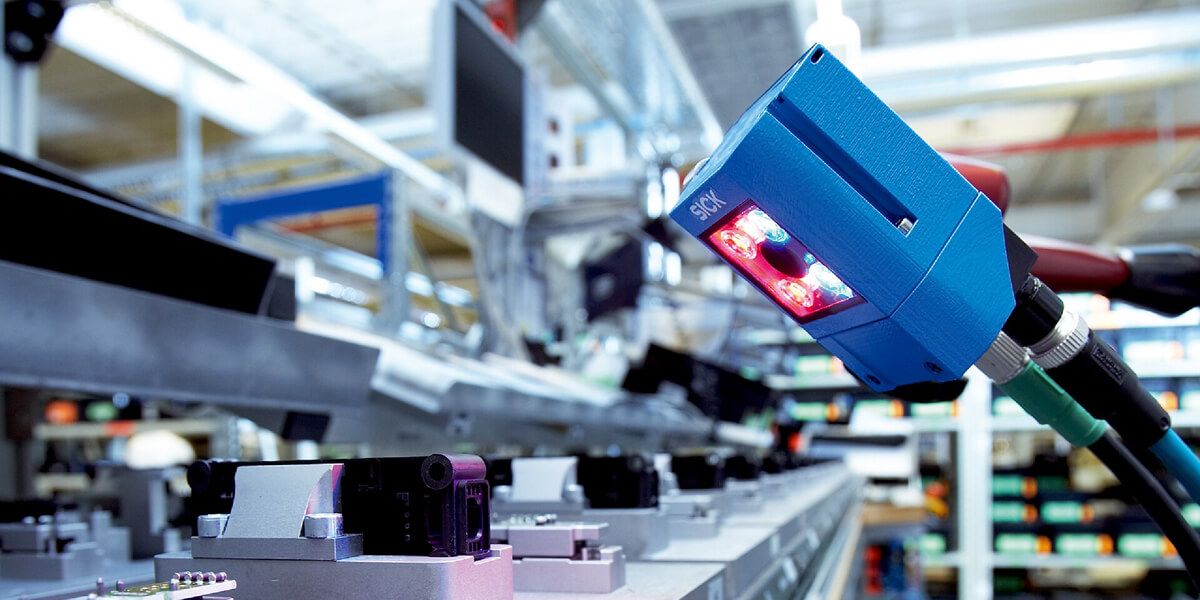
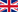
In general, the industry, as well as the production stages from product packaging to transportation to the final product warehouse, are experiencing a transformation due to the advancements in Machine Vision technologies (Cameras - Volumetric - Fixed Position Scanners). The three main pillars driving this transformation are:
- Very powerful autonomous equipment with new capabilities due to continuous upgrades.
- Intelligent equipment, with advanced reading and processing algorithms, and multiple communication capabilities with other systems.
- Central equipment management platforms, with multiple easy configuration options and the ability to further utilize data produced by the equipment in real time
The main reasons for utilizing Machine Vision technologies are the automation of inspections and measurements, aimed at increasing overall productivity and ensuring product quality.
Machine Vision applications combine a wide range of equipment to achieve the desired solution, with the main categories being:
- High-resolution cameras with embedded intelligence and the ability to perform on-site, real-time data analysis (edge computing).
- Decoding scanners for reading and recording all types of barcodes, placed at specific points along production lines and factory spaces.
- Software for image analysis and processing for evaluating and using images captured by cameras and scanners.
- Sensors of various types for detecting presence, position, or issues.
- Specialized lighting to ensure better image quality.
By combining the above equipment with automation (PLC - SCADA) and computer systems (MES - WMS - ERP), the automation of production processes is achieved.
Applications of Machine Vision Technologies
1. Printing Verification and Confirmation
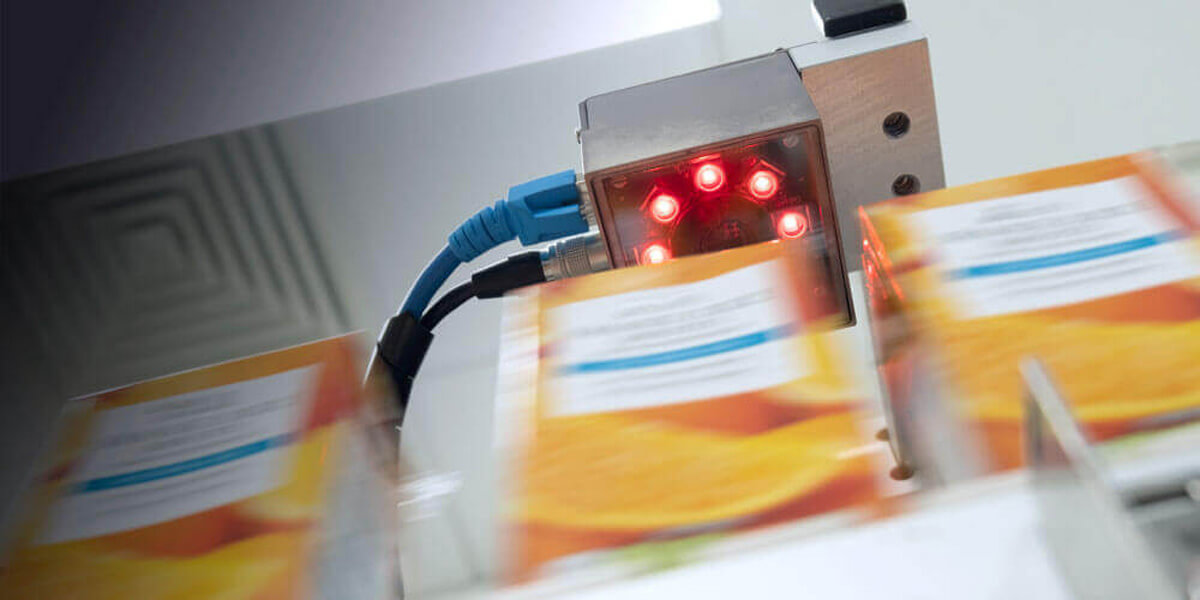
Like most applications, printing verification and confirmation comes in levels, depending on the need and desired result. The levels are as follows:
- Printing confirmation: Checking for barcode existence by reading it, without further processing or verification. Goal: Ensure the presence of labeling and readability.
- Barcode printing verification: Checking printing quality, barcode calibration (grading), and checking based on predefined rules (set length - special characters). Goal: Ensure proper labeling and the correct information transfer to other systems..
- Message printing verification: Camera communication with printer driver software to check successful printing of a message on the packaging, based on camera training for each message. Goal: Full message printing verification using OCR (Optical Character Recognition) and OCV (Optical Character Verification) algorithms.
2. Serialization & Aggregation

These are applications where labeling is done according to regulations and/or internal procedures, with verification and recording of labeling at multiple packaging levels. For this functionality, both scanners and cameras are used for control and data recording. Additionally, these Machine Vision systems communicate with PLCs and software, through which records and checks are made in databases, and non-compliant products are rejected.
3. Orientation and Labeling Check

Using cameras in collaboration with sensors and PLCs to detect container orientation and ensure proper alignment before applying the label, as well as verifying correct positioning after labeling. Goal: Ensure correct labeling and alignment for quality assurance and marketing purposes.
4. Orientation and Laser Marking Check
Handling high-speed production lines with random orientation, detecting orientation using cameras, and automatically marking based on product label design. Goal: Serve producers where physical/mechanical orientation is not possible, ensuring correct labeling for quality assurance and marketing purposes.
5. Correct Filling Check

Detection of fill level through Machine Vision or volumetric sensors to ensure each package contains the product within predefined limits. Goal: Prevent underfilled or overfilled items.
6. Product Quality Check
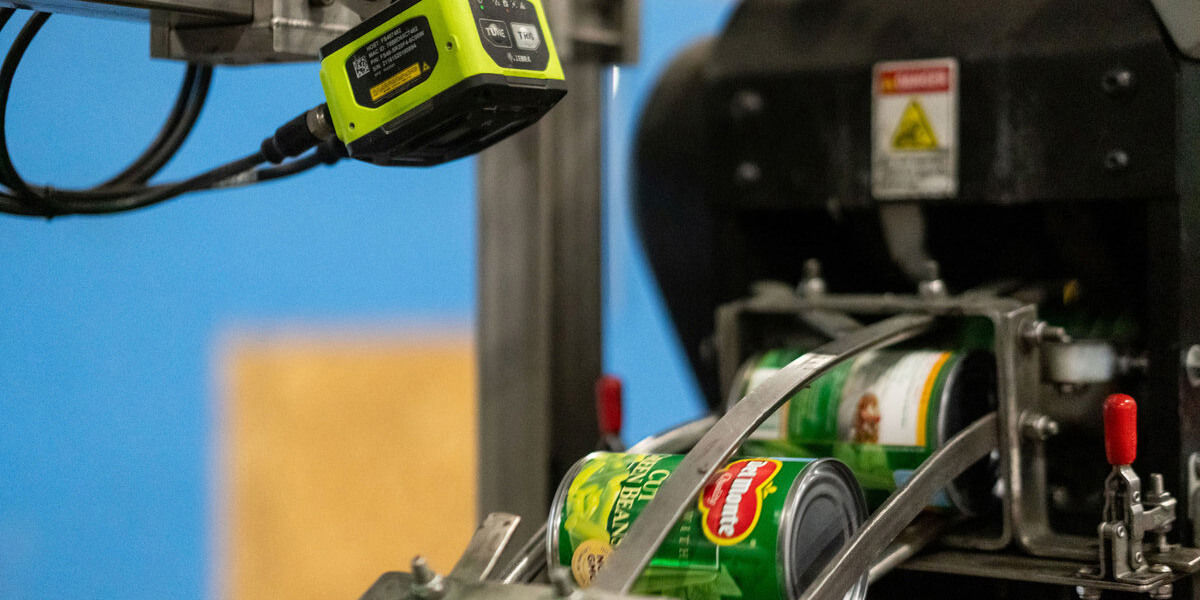

Using cameras to evaluate color, size, proper sealing, and tamper evidence, with the use of advanced image analysis algorithms and real-time image recording at high production speeds. Goal: Ensure overall product quality and packaging safety.
7. Volumetric Measurement - Counting and Classification by Dispatch Stations
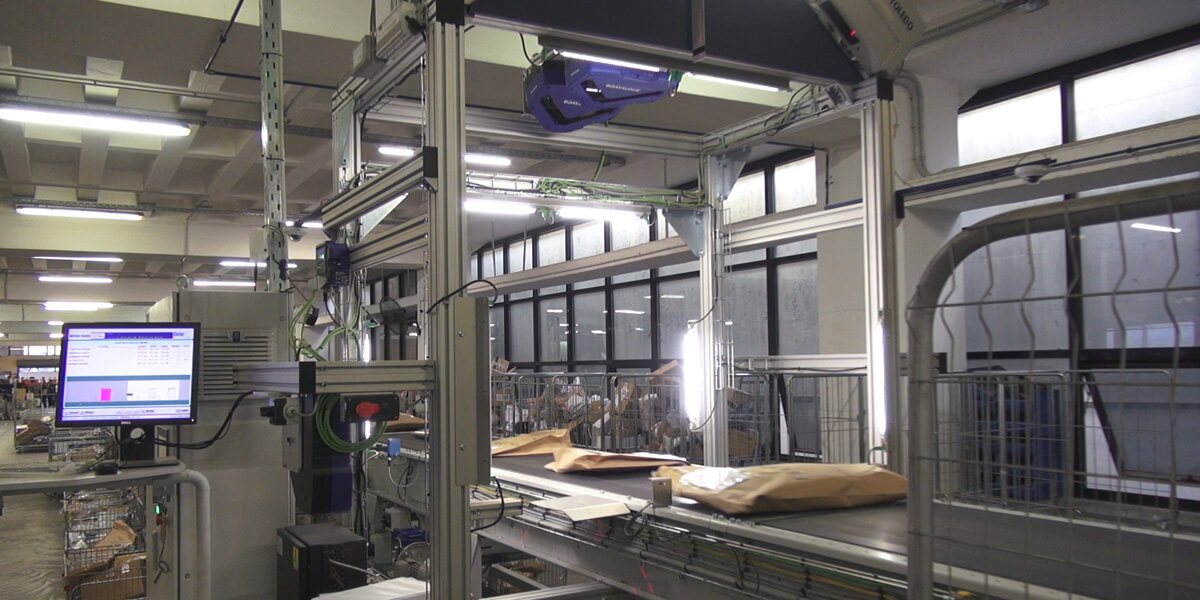

Detecting volume and measuring dimensions for proper sorting of parcels in courier services, as well as taking photographs for traceability and parcel status, using cameras. Goal: Faster and more accurate parcel sorting, improving sorting time and significantly increasing the volume of parcels processed.
8. Sorting and Central Palletizing of Products
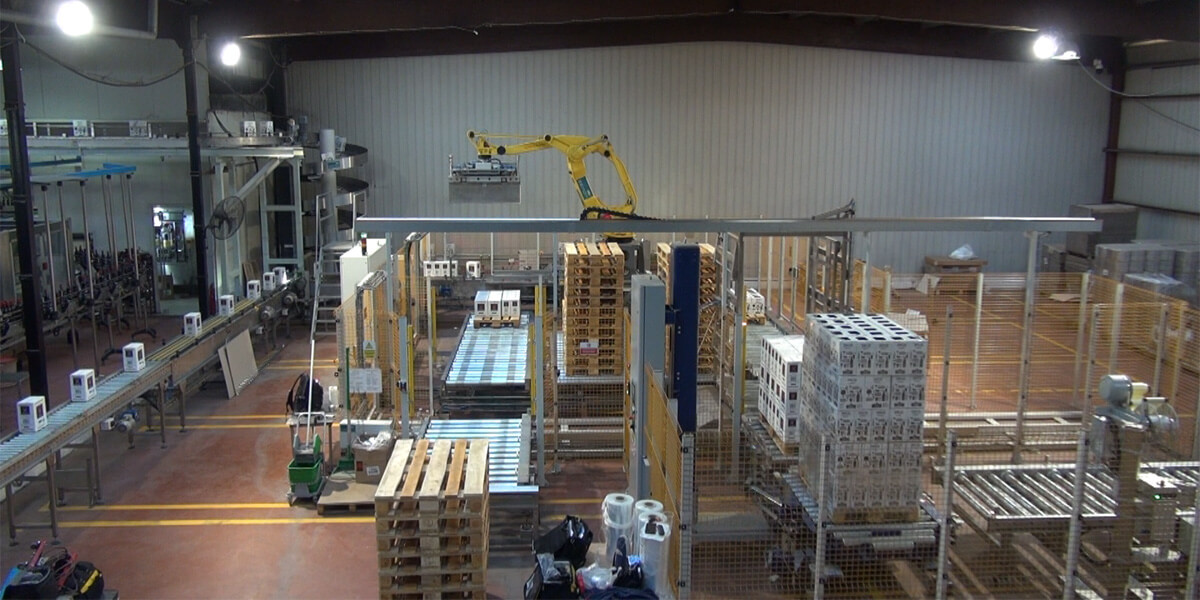

Using multiple fixed position scanners and cameras for full control and efficient movement of packages from the individual item level to pallet creation. At each packaging stage, Machine Vision systems, in collaboration with automation systems and production management software (MES), perform necessary processes (inspections and rejections, sorting, aggregation of packages, sorting of packages and boxes by final palletizing position).
By executing the above, "smart" central palletizing is achievable. Goal: Smart and fully dynamic central palletizing, with excellent benefits for the factory, such as installing less handling equipment and fewer robots, central management and supervision of palletizing across multiple production lines, and ensuring properly packaged and labeled products.
9. Bulk Packaging Check (Boxes - Pallets)
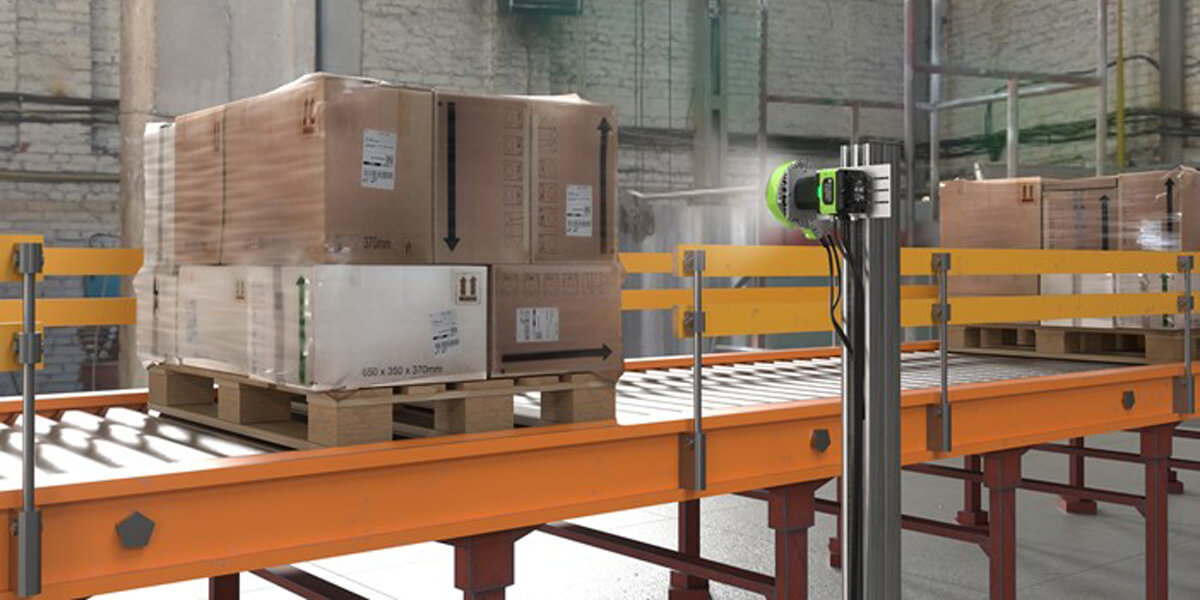

Using fixed position cameras during bulk packaging handling, with visual quality inspection of the external packaging for defects (box distortion, incomplete pallet wrapping, etc.), as well as quantitative checking of box contents with a count of items within the box.
Additionally, using these cameras ensures the maintenance of a digital image archive, recording the packaging condition before it proceeds further in the supply chain. Goal: Ensure the quality of bulk packaging, reject non-compliant packaging at its source, and maintain a digital archive for the condition and traceability of packaging within the factory..
Conclusion
Machine Vision technologies have become an integral part of modern industry, automating critical processes and enhancing efficiency, quality, and traceability of products. The continuous development of image analysis algorithms, combined with the ability to communicate with other industrial systems, makes Machine Vision solutions essential in every modern production and storage facility. Their integration into production lines not only improves quality but also provides significant competitive advantages, creating a more flexible, intelligent, and efficient operating environment..
 Giannis Maravelias is Consultant Engineer, Production Management Systems in Theodorou Group. He is responsible for digital transformation projects and the application of IoT technologies in industries. He holds a degree in Production and Management Engineering from the Technical University of Crete. He has been a business consultant with experience in process re-engineering.
Giannis Maravelias is Consultant Engineer, Production Management Systems in Theodorou Group. He is responsible for digital transformation projects and the application of IoT technologies in industries. He holds a degree in Production and Management Engineering from the Technical University of Crete. He has been a business consultant with experience in process re-engineering.