Dr. Evangelos Theodorou
Theodorou Group Chairman & CEO
 It is generally accepted that the supply chain is a complex system that “touches” many “stakeholders”: companies involved in the management of raw materials, production, processing and packaging of products, storage and distribution, transport, retail stores and of course the final consumers. For this reason it is particularly important that it functions correctly in all its stages, i.e. with maximum speed, zero to minimal errors, flexibility, with the necessary synchronization, the lowest possible cost, abundant information and transparency.
It is generally accepted that the supply chain is a complex system that “touches” many “stakeholders”: companies involved in the management of raw materials, production, processing and packaging of products, storage and distribution, transport, retail stores and of course the final consumers. For this reason it is particularly important that it functions correctly in all its stages, i.e. with maximum speed, zero to minimal errors, flexibility, with the necessary synchronization, the lowest possible cost, abundant information and transparency.
Over the past two decades, significant steps have been taken to modernize the supply chain resulting in significant cost reductions and increased productivity. It is predicted that these modernization trends will intensify in the next five years and that the supply chain will evolve into an important source of added value for businesses.
The catalyst is the fact that we now have at our disposal technologies, affordable and depreciable, that can be adapted to all sizes of businesses. These technologies can bring order to the complex supply chain environment by offering solutions for its control and management.
The technologies
One technology that is at the forefront of supply chain developments is the cloud, an increasingly accepted technology that enables the secure storage of large volumes of data.
At the same time, the internet of things (IoT) is entering our lives at an unimaginable pace. The IoT offers a large number of stakeholders access to a vast amount of information and is expected to revolutionize not only the operation of the supply chain, but also the way business decisions are made and consumer behavior.
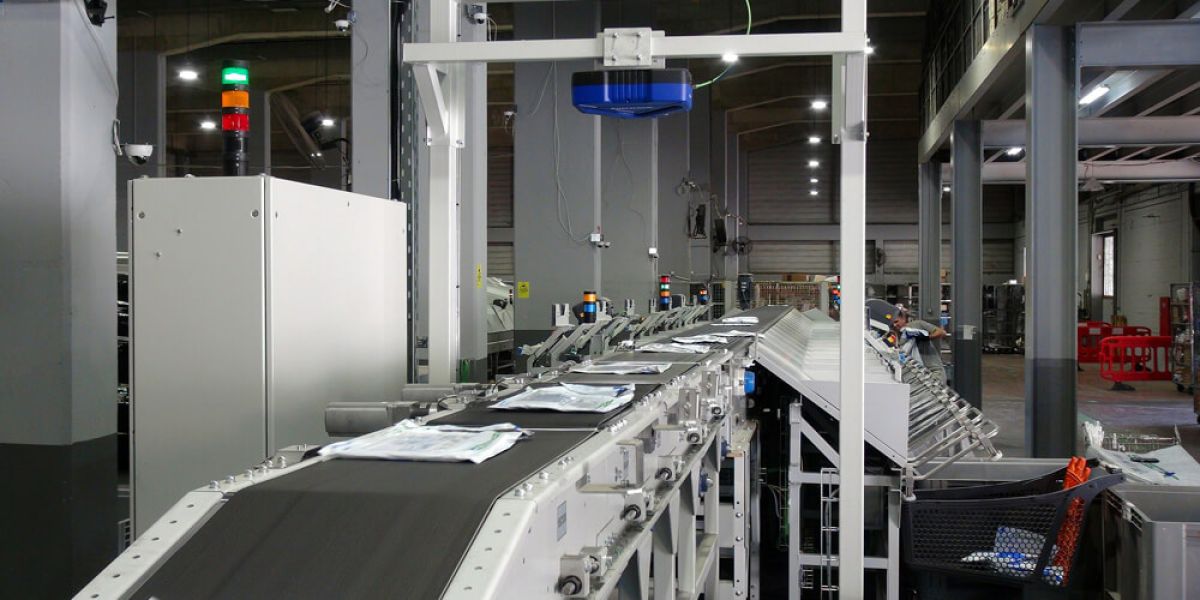
In addition, robotics is a mature and accessible technology and offers a multitude of applications for manufacturing as well as warehousing and shipping products. At the same time, motion and automation technology offers us intelligent handling and sorting systems that dramatically increase productivity in supply chain processes.
Data collection and processing technologies, such as mobile terminals and tablets and barcode readers, wireless networks, and RFID technology will play a catalytic role in the new trends. These systems now offer faster speeds, ease of use, security and excellent connectivity. The above offer a great improvement in productivity and error reduction. Wireless networks handle larger amounts of data with greater security, faster speeds, and lower costs.
The technology of coding and printing labels, which ensures the necessary information in the supply chain, is mature and can be ideally combined with the above. Finally, the development of specialized IT solutions for the management of production and storage offer significant cost reduction and process optimization.
New technologies are creating trends that will transform the supply chain in the near future. Below we summarize the main trends.
The trends
Reduction of links
The classic links of the supply chain are the receipt and management of raw materials, the production and processing of products, storage, distribution, transportation and the point of sale. The current trend is to reduce these links for obvious reasons of reducing resources and increasing speed. A typical example is that in industrial production, more and more companies are adopting the practice of direct shipping, i.e. sending products to large customers directly after the end of the production line without the intermediary of the warehouse. At the same time, practices such as cross docking drastically reduce the time the products stay in the warehouse, significantly speeding up shipments. Finally, the e-commerce analyzed below is another typical example of this trend.

Transparency
A very important trend affecting the supply chain is the growing need for transparency – from raw materials to the shelf. Legislation requires better and more accurate tracking of products at all stages of the supply chain, especially in the food and pharmaceutical sector (serialization). However, beyond the requirements of the legislation, the companies in the field want to satisfy their internal needs as well as the demands of their customers to ensure the quality and safety of the products. For this reason, they adopt reliable solutions and traceability systems that offer visibility and process optimization as well as crisis management.
E-commerce
The boom in e-commerce is yet another major trend that is drastically changing processes in product warehousing and distribution. This development is inextricably linked to the dramatic change in the preferences and demands of end consumers observed in recent years. Consumers are highly informed and prefer alternative methods of shopping, mainly via the internet. The immediate consequence is that the volume of products delivered directly to end consumers increases drastically. At the same time, the demand for same-day or next-day product delivery has increased both for end consumers and for business-to-business transactions. As a result of the above, e-commerce is expected to skyrocket in the near future and will highlight the warehouse and distribution centers, as critical hubs for e-commerce, in critical centers of added value and business development.
Automation and flexibility
Companies operating in the supply chain have a perennial need to be more competitive and to continuously reduce their costs by improving their processes. At the same time, as the operation of the supply chain is highly complex and the demands of customers are many and specialized, the need for flexibility is greater than ever. In recent years, technologies such as robotics, coding, IT and mobility have become accessible and adaptable to the data of each business and satisfy the above needs through the automation of processes at all stages of the supply chain. The processes that are automated cover the production and packaging of the products, the storage and the execution and shipping of the orders, the quality control and the monitoring of the production process. A typical example is the adoption of automatic order fulfillment systems in applications such as the shipment and distribution of medicines. Pharmacies are required to serve thousands of customers every day by fulfilling dozens of orders consisting of dozens of disparate product codes. Through the automation of processes they achieve an impressive increase in their productivity and flexibility.

Mobile Worker
A recent trend dominating the supply chain is that devices are now connected and the amount of information available about products is growing exponentially. Characteristically, the vast majority of data currently available worldwide was created in the last two years. There is a need to disseminate, utilize and manage this information. And of course, it is especially important that intra-business systems are completely synchronized and even in real time. The goal is for a business to have access to the right information at the right time, to analyze it, to make the right business decision, to be able to execute it with visible and measurable results. The above needs, catalyzed by cloud, IoT and mobility technologies, have created the trend for “mobile” workers, i.e. workers who have access to information from any location, who are “close” to the information at the moment it is born.

The above makes the supply chain a very complex and evolving environment, to which the companies involved in each stage of the chain are required to adapt. The companies that understand the current trends and adapt faster will be the ones that will be able to gain a competitive advantage and survive more easily.
 Dr. Evangelos Theodorou is the President & CEO of Theodorou Group. He holds a degree in Electrical and Mechanical Engineering – NTUA (National Technical University of Athens) and holds a Ph.D. in Electronic Systems from the University of Cambridge, England. He has been a lecturer at the Department of Electrical and Mechanical Engineers of the NTUA.
Dr. Evangelos Theodorou is the President & CEO of Theodorou Group. He holds a degree in Electrical and Mechanical Engineering – NTUA (National Technical University of Athens) and holds a Ph.D. in Electronic Systems from the University of Cambridge, England. He has been a lecturer at the Department of Electrical and Mechanical Engineers of the NTUA.
Warehouses / Supply Chain